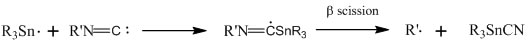Nachtisch (Dessert)
Common German desserts: Schwarzwald Torte (Black Forest Cake), Haribo Gummibaerchen (Gummy Bears), und Kuchen (cake).
Leading Questions (part d)
Main Paper:
Saegusa, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Ito, Y.; Yasuda, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 90, 4182.
Three papers from this paper:
Thayer, J. S.; West, R. Advan. Organometal. Chem. 1967,5, 183.
This paper was cited because it explains how, through infrared spectroscopy, cyanide is formed more than isocyanide in a 10:1 ratio. However, the paper states that it is uncertain to whether the cyanide form and isocyanide form are in equilibrium.
Reviewed by Kuivila, H. G. Advan. Organometal. Chem. 1964, 1, 47.
This paper was cited because it explains how trialkyltin hydride is prepared and, in further pages not actually cited, it gives experimental evidence of reactions with organotin hydrides with the use of catalytic azobisisobutyronitrile (page 61) and a proposed mechanism on page 64.
Saegusa, T.; Ito, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Hirota, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89,2240.
This paper was cited for its work with inserting isocyanide into a silicon—hydrogen linkage using a copper catalyst. This copper catalyst did not work to insert isocyanide into the tin—hydrogen linkage, which was the reason to find a new radical reaction of isocyanide with trialkyltin hydride.
Other two papers:
Gentric, L.; Hanna, I.; Ricard, L. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 1139–1142.
Fukuyama, T.; Chen, X.; Peng, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, 3127–3128
The reaction scheme which this paper has suggested for the reaction between tri-n-butyltin and isocyanide is the following:

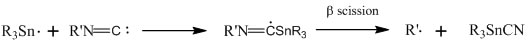

This reaction was experimentally proven multiple times. One experiment run was the reaction of benzyl isocyanide, tri-n-butyltin hydride, and di-t-peroxide. One product from this reaction was tri-n-butyltin (iso)cyanide. In the next two reactions referenced by this paper, the paper states that the use of azobis(isobutyronitrile) was needed to initiate the free-radical. The azobis(isobutyronitrile) reacts with the tri-n-butyltin hydride to form the free radical of tri-n-butyltin. However, this reaction is not shown in this paper. This radical then reacts as shown above in the reaction scheme proposed. One of the two reactions in this article, of cyclohexyl isocyanide and tri-n-butyltin hydride, produced 52% tri-n-butyltin (iso)cyanide and 47% of cyclohexane. As stated in the article, in the reaction of t-butyl isocyanide with tri-n-butyltin hydride with the help of azobis(isobutyronitrile) the products were isobutene (45% yield) and tri-n-butyltin (iso)cyanide. Therefore, the conclusions made by this paper are that the reaction of tri-n-butyltin hydride with any isocyanide source produces tri-n-butyltin (iso)cyanide and a hydrogen where the isocyanide was connected to the other molecule.
Part (e)
Three alternative reagents for phosgene are 1,1-carbonyldiimidazole, diphosgene, and triphosgene:

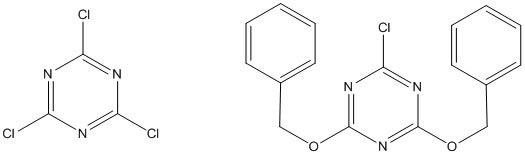
Two alternative reagents for 2-chloro-4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazine (CDMT) are 2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine (also known as cyanuric chloride) and 2-chloro-4,6-dibenzyloxy-1,3,5-triazine:
Two alternative reagents for triethylamine are tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) and N,N-diisopropylethylamine:

Three alternative reagents for NMM are DABCO, N-methylpiperidine, and N-methylmorpholine:

One alternative reagent for is tristrimethylsilylsilane (TTMSS):

One alternative reagent for formic acid is trifluoroacetic acid (TFA):